Description
When exporting a high-order (H-O) mesh, the Export CAE panel (shown below) is modified slightly to provide feedback on the smoothing and elevation
process. Note that due to the nature of polynomial elevation, producing a high-order mesh can be a lengthy process for larger grids.
Caution: Due to the nature of polynomial elevation, producing a high-order mesh can be a lengthy process for larger grids.
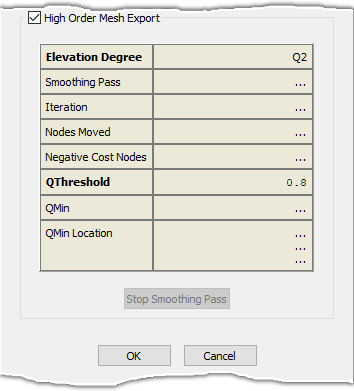
The Export CAE panel changes when exporting a high-order mesh.
The elevation process consists of two primary phases: the WCN Smoothing phase and the curving phase. The curving phase itself usually includes two
sub-phases, but may have as many as four.
As the elevation process proceeds, the minimum curving cost value factor, QMin, should be positive and the
closer it approaches 1 the better. Monitoring QMin with each iteration provides you with feedback on the appropriateness of the inputs set
in CAE, Set Solver Attributes. For example, oscillation that may appear in the minimum
curving cost value factor can be indicative of a Step Size Relaxation Factor that is too large. One active control, Stop Smoothing Pass, is
provided to halt the smoothing process. The stop sign icon present in the progress bar area of
the Status Bar can be used to halt the elevation process.
Note: Note that solver attributes, including polynomial degree elevation, are available
in CAE, Set Solver
Attributes for CAE formats that support high-order export.
When exporting a high-order mesh, please note the following:
- The elevation process matches high-order nodes across periodic boundary pairs.
- Elevation of non-planar boundaries differs based on whether the domain is database
constrained or not. If the domain is database constrained, the high-order nodes are placed
on the underlying database. However, if the domain is free, the high-order nodes are
positioned using linear interpolation.
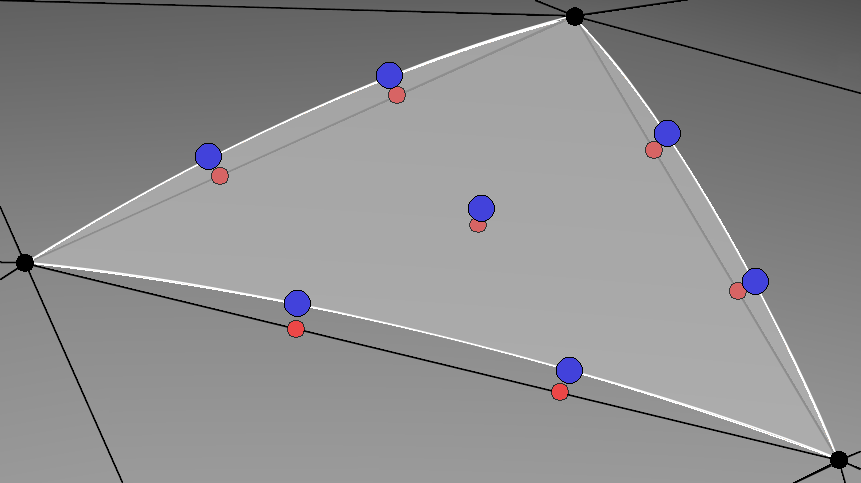
The high-order nodes are placed on the underlying database (shown in blue) or, if the domain
is free, using linear interpolation (shown in red).
- The elevation process does not currently support domains that are part of baffles or are not
fully constrained on their interior. The elevation process will be aborted
and an error will be issued if either of these types of domains are detected.
An error message is printed out in the Display window if the elevation process detects a
baffle domain (left) or a domain that is not fully constrained on
its interior (right).
Note: Many issues with high-order export can be traced back to poor
projections. Make sure that each surface domain and connector is constrained to a minimum
number of database entities (instead of all database entities). For domains, this can be
done from the Attributes Tab in the unstructured
domain
and
structured
domain
solvers. For connector projections, it is also recommended to use the Project Shape option in
the
Projection Control frame.