Description
The controls in the Smoothing frame allow you to set a desired quality threshold, specify which cells are selected for smoothing, and improve the stability of the Weighted Condition Number smoothing routine.
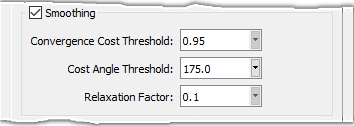
The Convergence Cost Threshold allows you to specify a maximum threshold value for the minimum quality cost function and stops the smoothing routine prior to reaching the number of iterations specified on the Solve Tab if this maximum is achieved. The Convergence Cost Threshold varies from 0.0 to 1.0 and has a default value of 0.95.
Note: The Cost Angle is an alternate form of the Maximum Included Angle. The Cost Angle computes a face normal for each corner of a quadrilateral cell face whereas the examine metric uses a single face normal computed from the two quadrilateral face diagonals. The Cost Angle takes longer to compute, but is more accurate because it accounts for quadrilateral warpage. This ensures all cells with large maximum included angles are smoothed.
The Cost Angle Threshold sets the angle to determine which cells in the mesh receive smoothing. Cost Angle Threshold varies from 0.0 to 180.0 and has a default value of 175.0. A value of 0.0 enables a special mode that uses the ideal isotropic tetrahedral shape as the target for each cell.
Tip: Using a value of 0.0 for Cost Angle Threshold enables a special smoothing mode that uses the ideal isotropic tetrahedral shape as the target for each cell. This is extremely useful for smoothing blocks that contain only isotropic tetrahedra, but is not recommended for blocks containing all cell types, T-Rex layers, or voxels.
The Relaxation Factor is used to limit grid point movement during smoothing to improve stability. Relaxation Factor varies from 0.0 to 0.5 and has a default value of 0.1.